how is hardness tested on a mineral|hardness scratch test : factories The Mohs Hardness Test is almost exclusively used to determine the relative hardness of mineral specimens. This is done as part of a mineral identification procedure in the field, in a classroom, or in a laboratory when easily identified . Live Soccer TV - Football TV Listings, Official Live Streams, Live Soccer Scores, Fixtures, Tables, Results, News, Pubs and Video Highlights
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 11 de mai. de 2023 · To achieve his goal, he became an assistant to the famous warrior Thor. When the fearsome dungeon of the Mad Gate awoke from its slumber, Aeon teamed up with Thor and the world’s most powerful explorers to conquer it. Unbeknownst to them, they were unwitting victims .
If you want to identify a mineral, a hardness test can give you valuable information. You'll probably need to do a scratch test to in order to find what minerals are harder than your sample. Then, you can refer to the Mohs hardness scale, which ranks common minerals by hardness. See more Apatite (Hardness 5): Apatite is a common mineral in rocks and is often green. It can scratch fluorite and is frequently used in fertilizers due to its high phosphorus content. .The Mohs Hardness Test is almost exclusively used to determine the relative hardness of mineral specimens. This is done as part of a mineral identification procedure in the field, in a classroom, or in a laboratory when easily identified . One key to identifying mineral species is to test its hardness. Mineral hardness tests can be performed at home or on a rockhounding field trip. There are necessary tools for express hardness testing: A fingernail, a .
The Mohs Hardness Test is a simple procedure to gauge the scratch resistance of minerals. To perform the test, an examiner attempts to scratch the mineral in question with a .
The Mohs test is one way to determine the hardness of a rock or mineral. You can use the test to help identify an unknown specimen.Mohs Hardness Testing Procedure. To perform a Mohs hardness test, you will need a set of Mohs minerals, a sample of the unknown mineral, and a clean, flat surface. Here's the basic .
A simplified and crude test for hardness is to test whether or not a sharp corner or edge of a sample scratches (or indents) a glass plate. A numerical reference scale for hardness was . The Mohs hardness scale is a qualitative test that measures the hardness of a mineral by its ability to visibly scratch softer minerals. The scale isn’t perfect, but it’s a great tool for quick identification of rocks in the field.
updated mohs scale of hardness
Hardness (H) is the resistance of a mineral to scratching. It is a property by which minerals may be described relative to a standard scale of 10 minerals known as the Mohs scale of hardness. The degree of hardness is . This video shows the steps needed to determine the hardness of a mineral. The Mohs hardness scale rates the hardness of minerals based on their ability to scratch softer ones. The Mohs hardness scale is a qualitative test that measures the hardness of a mineral by its ability to visibly scratch .
The Mohs scale is only one of a number of scales used to assess mineral hardness. Others include the Vickers scale, Brinell scale, Rockwell scale, Meyer hardness test, and Knoop hardness test. While the Mohs test .
The Mohs Hardness Test is a simple procedure to gauge the scratch resistance of minerals. To perform the test, an examiner attempts to scratch the mineral in question with a reference mineral or material from the Mohs Scale. If the reference substance scratches the test specimen, the test mineral has a lower hardness rating.

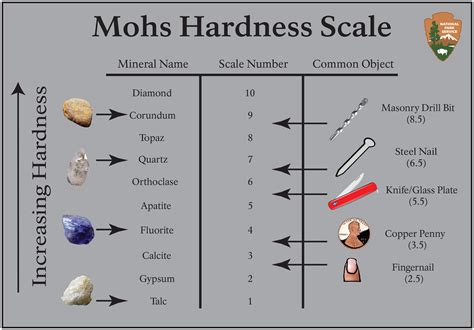
Additional Rocks. Shale: 2-3 (very soft, easily scratched) Limestone: 3 (scratched by copper penny) Marble: 3-4 (softer than granite, often used in sculpture) Slate: 3-5.5 (depending on composition) Granite: 6-7 (hard, durable, used in countertops) Basalt: 5-6.5 (volcanic rock) Hardness Variations in a Single Mineral. It is essential to note that hardness can vary within .Determining the hardness of an unknown rock or mineral is often very useful in the identification process. Hardness is a measure of a mineral's resistance to abrasion and is measured against a standard scale - Mohs Scale of Hardness. Mohs Scale was named after Frederick Mohs (1773-1839), a German minerologist. It consists of 10 fairly common minerals (except for the .Mohs hardness kit, containing one specimen of each mineral on the ten-point hardness scale. The Mohs scale (/ m oʊ z / MOHZ) of mineral hardness is a qualitative ordinal scale, from 1 to 10, characterizing scratch resistance of minerals through the ability of harder material to scratch softer material.. The scale was introduced in 1812 by the German geologist and mineralogist .The Mohs scale of mineral hardness is based on the ability of one natural sample of mineral to scratch another mineral visibly. The hardness of a material is measured against the scale by finding the hardest material that the given material can scratch, or the softest material that can scratch the given material. . The Knoop hardness test .
MINERAL HARDNESS SCALE: compares the resistance of a mineral to being scratched by 10 reference minerals - makes hardness a reliable diagnostic property - fingernail = 2.5, copper penny = 3.5, steel nail = 4.5, glass plate = 5.5, streak plate = 6.5 Hardness Scale: 1) Talc 2) Gypsum 3) Calcite 4) fluorite 5) Apatite 6) Feldspar 7) Quartz 8) Topaz 9) Corundum 10) . The Mohs hardness test kit is a scratch-testing kit with all the minerals in the Mohs Hardness Scale except diamond. Why? . Some mineral’s hardness varies with the direction of scratching. For some minerals, the hardness may depend on the direction of your scratch or crystal face. A good example is the kyanite mineral.A mineral is struck with a metal rod or "testing mineral" to test its hardness. It is tested in the manner of the following example: Action: Conclusion: Mineral struck with rod or mineral number 4 (Fluorite) from the testing kit. Mineral gets scratched. For hardness testing, non-mineral substitutes can be used to represent the various levels of the Mohs scale: Copper Wire: With a hardness of approximately 3.5, copper wire is a versatile tool for assessing a mineral’s hardness. It can scratch softer minerals like talc, gypsum, and calcite but won’t leave a mark on harder minerals like .
No headers. Hardness is a mineral’s resistance to abrasion or scratching. We determine relative hardness (symbolized by H) using a scratch test: we try to scratch a surface of one mineral with an edge or corner of a second mineral.If a scratch or abrasion results, the first mineral is the softer. Absolute hardness is not quite the same as relative hardness.Hardness testing within the realm of materials testing. Today, hardness testing is one of the most widely used methods in mechanical materials testing, especially for metals. On the one hand, this test method can be used to find qualitative relations to other material properties (e.g., strength, stiffness, density) or to the material behavior under certain stresses (e.g., abrasion .To test your mineral’s hardness, you’ll want to attempt to scratch the mineral with the items above, or vice versa. I like to start in the middle of the hardness scale, so I usually try to scratch my glass plate with the mineral. If the mineral . Hardness is measured on the 10-point Mohs scale, which is essentially a scratch test. Take an unknown mineral and scratch it with an object of known hardness (like a fingernail or a mineral like quartz.) Through trial .
With a Mohs scale, anyone can test an unknown mineral for its hardness. Imagine you have an unknown mineral. You find that it can scratch fluorite or even apatite, but feldspar scratches it. You know then that the mineral’s .
Mineral hardness is defined as the relative ability of a mineral to resist scratching or abrasion. The first attempt to quantify the hardness of a mineral for which there is any record was made in 1812 by Friedrich Mohs, a German geologist and mineralogist. . The Mohs Scale and its application to testing mineral properties is the subject of .
With a Mohs scale, anyone can test an unknown mineral for its hardness. Imagine you have an unknown mineral. You find that it can scratch fluorite or even apatite, but feldspar scratches it. You know then that the mineral’s hardness is between 5 and 6. Note that no other mineral can scratch diamond. Mohs hardness scale was devised in 1812 by Friedrich Mohs and has been the same ever since, making it the oldest standard scale in geology.It is also perhaps the most useful single test for identifying and describing minerals.You use the Mohs hardness scale by testing an unknown mineral against one of the standard minerals.With a Mohs scale, anyone can test an unknown mineral for its hardness. Imagine you have an unknown mineral. You find that it can scratch fluorite or even apatite, but feldspar scratches it. You know then that the mineral’s hardness is between 5 and 6. Note that no other mineral can scratch diamond. Cleavage and Fracture
For a more specific method: one would scratch the mineral to be tested against the standard hardness on the Mohs hardness scale to determine the hardness of the tested mineral. For example, if a mineral can scratch calcite and be scratched by fluorite, then the hardness of that mineral is between 3 and 4.The "streak test" is a method used to determine the color of a mineral in powdered form. The color of a mineral's powder is often a very important property for identifying the mineral. The streak test is done by scraping a specimen of the mineral across a piece of unglazed porcelain known as a "streak plate." This can produce a small amount of .
The Vickers Hardness Test. The Vickers Hardness Test, sometimes termed as microhardness test, utilizes a diamond indenter with a square-based pyramid shape. The test measures the diagonal length of the indentation left after applying a specific load to the material for a set duration. The Vickers Hardness Value (HV) is then calculated using a .When testing the hardness or streak or other property of a mineral, the best way to test is on a freshly broken surface with expected luster that has not been exposed to weathering. Hardness, Toughness, and Strength When testing for hardness, remember that you are testing "the resistance to scratching." DuringHardness picks make hardness testing a more precise process - especially when testing small specimens or mineral grains within a rock. The point of the pick can easily be placed on the part of the specimen that you want to test. The scratches that you make or trails of metal that are left behind are usually very easy to distinguish. Check our step-by-step DIY Guide: Testing Mineral’s Hardness (Explained by Expert) or Performing Scratch Test on Rocks (Follow These 8 Steps). Mineral samples have to be clean and dry. Avoid weathered surfaces for testing as they have different physical properties and can confuse you.
matrix t test package
mantel test r package
Resultado da Traduce texto y archivos completos de manera instantánea. Traducciones precisas para particulares (un solo usuario) y equipos de trabajo. Millones .
how is hardness tested on a mineral|hardness scratch test